Blog
What are the Essential Nutrients?
What are the essential nutrients?
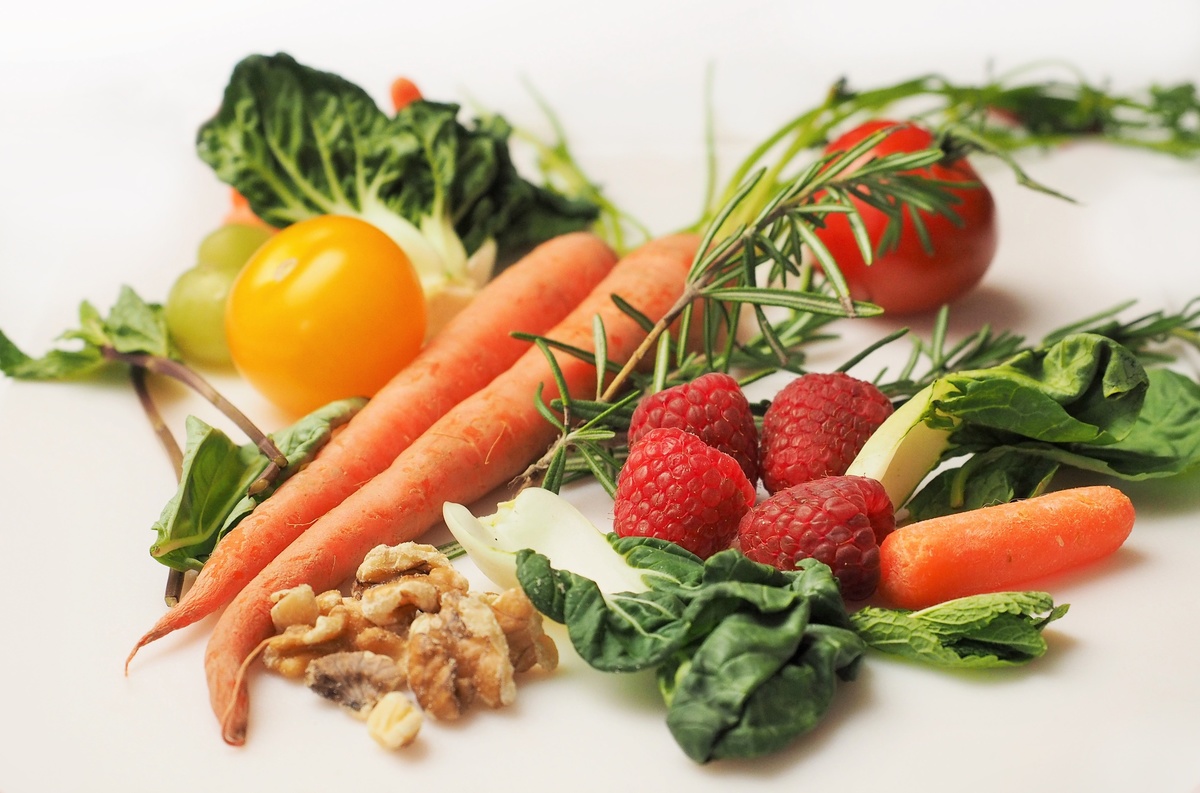
The term ‘nutrient’ refers to anything that offers nourishment which is crucial for growth as well as maintaining life. If we talk about ‘essential nutrients’, we’re referring to compounds that the body is unable to make or make in adequate quantities. According to the World Health Organization, essential nutrients must come from food. These are vital for the prevention of diseases, growth and good health.
The class of nutrients encompasses micronutrients and macronutrients, together with fatty acids and amino acids.
• Macronutrients are eaten in hefty amounts and include the key building blocks of your diet. These are nutrients such as protein, carbohydrates and fat that provide your body with energy.
• Vitamins and minerals are micronutrients. Small doses of these go a long way.
Many nutrients are good for us, however there are a few that we need to be particularly mindful of incorporating into our diets.
Protein
Protein is vital for good health as it provides the building blocks for the body and not merely for muscle. Every cell in the human body such as bone, skin and hair, contains protein. All of the hormones, antibodies, and other important substances in your body are made up of protein. Protein is not used as fuel for the body unless it is absolutely necessary.
Proteins are made of up various amino acids. While the body can make up some amino acids on its own, there are many critical amino acids which can only come from food. It is necessary to have a variety of amino acids for your body to work properly.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are require for your body to be healthy as carbs provide the fuel your body, especially your central nervous system (CNS) and brain. In addition, these help to protect against disease. According to medical experts, carbohydrates should make up between 45 and 65% of your total daily calories.
Fats
Believe it or not, healthy fats are a fundamental part of a healthy diet. It is recommended that you should be getting around 30% of your daily calories from fats. There are a several benefits to including healthy fats in your diet:
• Balancing your blood sugar,
• Decreasing your risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes,
• Improving brain function,
• Providing powerful anti-inflammatory properties, and
• Possibly lowering your risk of arthritis, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Harvard Medical School makes the statement that these kinds of fats are responsible for supporting a lot of your body’s functions, for example:
• The absorption of vitamins and minerals
• Blood clotting
• Building cells
• Muscle movement.
While fats may be higher in calories as opposed to other food groups, these calories are a vital energy source for your body.
Water
Maintaining your hydration levels is very important because this is absolutely essential for survival and water makes up to 60% of the human adult body. Several days with no water can lead to serious illness and even cause death. Our body depend on water as it is critical for waste removal and temperature regulation. In addition, it is an essential element of every cell as we’ve already alluded to.
To keep hydrated, drink water throughout the day. Eat foods with a high-water contents such as fruits and vegetables. Make sure that you keep drinks – such as coffee and soft drinks that will dehydrate you – to a minimum. However, don’t totally deny yourself these because if you do, and you start to crave them, you’ll probably overindulge. So, make sure that you control your consumption and keep it to moderate levels.
Vitamins
The term ‘vitamins’ refers to organic compounds which are essential for body:
• Growth
• Functioning
• Maintenance
• Repair.
There are two categories of vitamins: water soluble and fat soluble:
• Water-soluble vitamins which include the B complex group and vitamins C and need to be resupplied daily owing to the body’s inability to store them.
• Fat-soluble vitamins which include A, D, E, and K and are stored by the body for long periods of time.
This means that excessive intake of fat-soluble vitamins may be harmful.
A balanced diet should deliver all the vitamins which the body needs.
Minerals
The term ‘minerals’ refers to inorganic compounds which assist in energy production, body maintenance and helping in the control of body reactions.
The nutrient group consists of:
• Macro minerals
• Electrolytes
• Micro elements.
Macro minerals - such as calcium and magnesium - should be taken in larger doses. Examples of electrolytes are sodium, potassium, chloride as well as bicarbonate. The body requires very small amounts of micro minerals, for example chromium, cooper, fluoride, iodine, iron, magnesium, molybdenum, selenium, sulphur, and zinc. As if the case with minerals, a balanced and nutritious diet consisting of meats and vegetables can help you in meeting your daily vitamin intake.




Comments