Blog
What is a Healthy, Balanced Diet for Diabetes?
Most people understand that proper nutrition is vital for optimal health and functioning, but individuals who have diabetes may need to modify their diet beyond what is recommended for the typical person, in order to manage blood sugar levels and keep diabetes symptoms under control. If you have been living with diabetes for years and want to improve your health, or you have just received a diagnosis, it can be helpful to have some guidance regarding the best nutrition for you.
Here, learn about what constitutes a healthy, balanced diet for diabetes. Keep in mind that if you are seeking medical recommendations or advice regarding your unique health situation, it is important to reach out to your doctor or a licensed nutrition professional.
General Nutrition Guidelines for Diabetes
While everyone’s specific nutritional needs will vary based upon their overall health and lifestyle, there are some general dietary guidelines for individuals living with diabetes. According to the Cleveland Clinic, different diets will work for different people, but the following guidance is applicable for most people with a diabetes diagnosis:
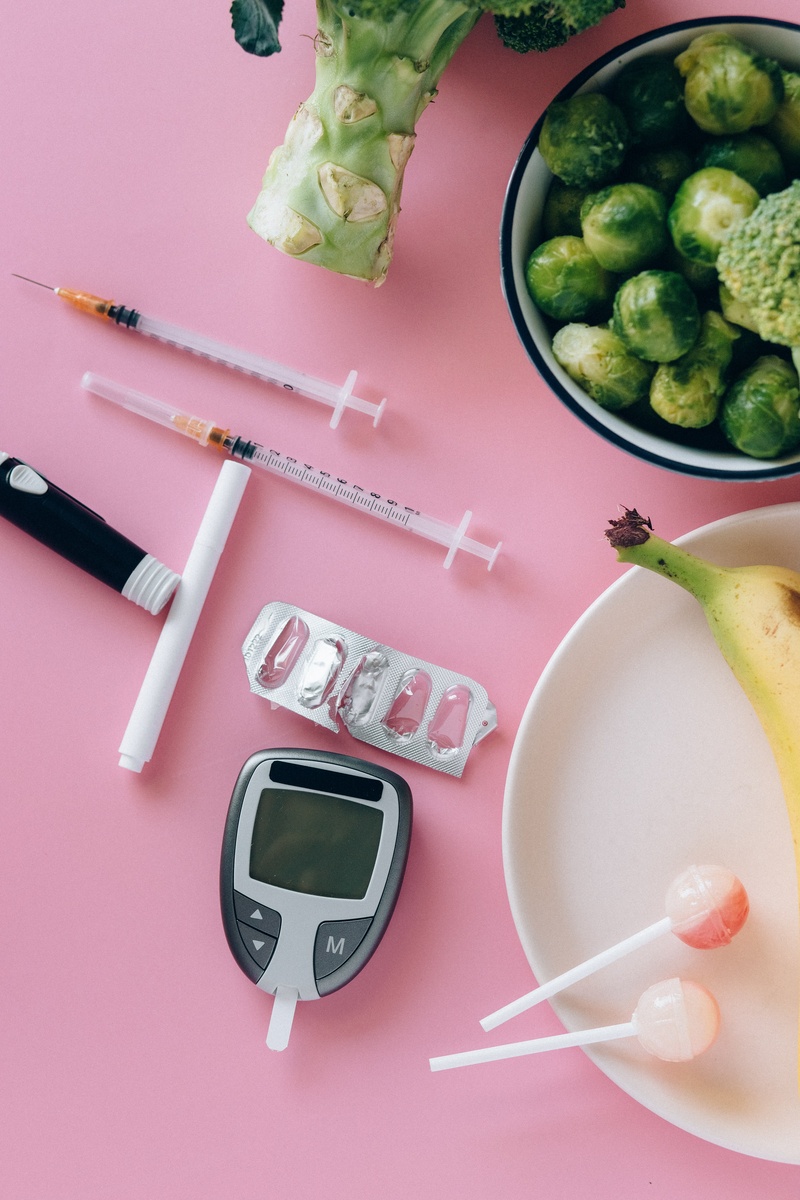
Non-starchy vegetables, such as broccoli and carrots, should be incorporated into the diet.
Those with diabetes should avoid foods that are high in added sugars.
Whole grain foods are preferable over highly processed grains.
Avoid sugar-sweetened beverages like sodas and juices, and stick to water.
Include as many whole foods as possible in the diet, and avoid highly processed and fried foods.
If you have diabetes, your doctor may recommend a weight loss diet to help you manage your blood sugar levels. Your physician or a nutrition professional can help you to determine the best weight loss diet for you.
A Balanced Diabetes Meal Plan
Your doctor or nutritionist may give you a meal plan to help you learn how to eat a balanced diet and keep your diabetes symptoms under control. In addition to following the guidelines above, your meal plan is likely to include a variety of nutritious foods from all the food groups. In many cases, you can still incorporate your favorite foods into your diabetes meal plan, but you may have to consume smaller portions than you usually would. In addition, highly processed and sugary foods may be limited, so you only consume them on occasion as a treat.
A diabetes-specific eating plan may include foods from the following groups, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases:
Non-starchy vegetables like carrots
Starchy vegetables like corn and potatoes
A variety of fruits
Proteins, including lean meats, turkey, chicken, fish, eggs, nuts, beans, and meat substitutes like tofu
Non-fat and low-fat dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt
Grains, with at least half being whole grain products
Ultimately, your doctor will work with you to ensure that your blood sugar levels are staying within an acceptable range, and that other areas of your health, such as your cardiovascular system, are in order. Your diabetes meal plan and your portion sizes may need to be adjusted, based upon how your body responds. For example, if your blood sugar is increasing, you may need to make changes to your diet to bring it back down to a healthier range. Furthermore, it is important that your healthy diabetes diet is combined with a lifestyle plan that includes regular exercise and adherence to your medication routine.
What does the research say?
While no single diabetes eating plan will be effective or appropriate for everyone, nutrition researchers have taken a look at various diabetes diets. Based upon the evidence, the following eating plans may be useful for patients with diabetes:
Low-glycemic diets: These types of diets are thought to reduce spikes in blood sugar levels, and they include whole grains, fruits, non-starchy vegetables, and healthy fats, while limiting potatoes, fruit juices, and white breads and pastas. Multiple studies have shown that low-glycemic diets are effective for weight loss, as well as for reducing fasting glucose, A1C, and cholesterol levels in those with diabetes.
Low-carb diets: A research review that assessed the results of 25 different studies found that low carb diets that restricted carbohydrate intake to a daily total of under 26% calories from carbs significantly reduced A1C levels after 3 and 6 months. Low-carb diets may not be safe or manageable for everyone, and the review found that they were not as effective over 12 and 24-month periods, so it is important to consult with a medical or nutrition professional before starting such a diet.
Other Diabetes Diets: The body of research has also found that the Mediterranean Diet, a Palaeolithic diet, and vegetarian diets were beneficial for diabetes.
What can be inferred from studies on diabetes diets is that there are a variety of eating plans that can be healthy, and help patients to manage their blood sugar levels. If you are living with diabetes, a medical professional can help you to devise a diabetes meal plan that meets your unique needs.




Comments