Blog
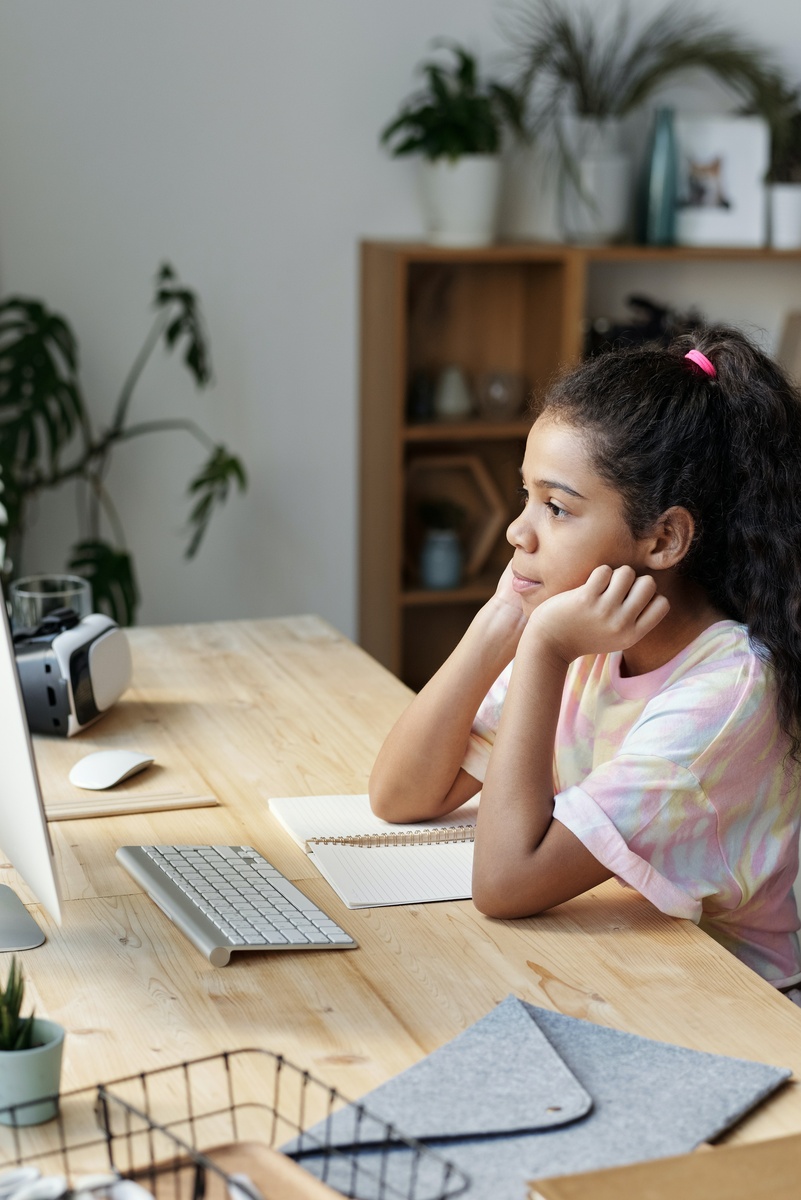
How to Teach Your Kids Online Safety and Responsibility
Digital technologies put a whole world of possibilities at our fingertips, offering us more opportunities than ever before to learn, exchange, participate and create.
However, on the internet, there are also dangers waiting for its users such as loss of privacy, cyberbullying, disinformation, or exposure to potentially harmful content. These can especially affect the most vulnerable users, such as children.
On many occasions, this is a particularly difficult task for parents who do not know how to teach their kids cybersecurity or online security measures children should take. For this reason, we want to contribute our grain of sand to this initiative by showing how to teach internet security to children.
Parental mediation for internet use:
To protect minors on the Internet, it is necessary to employ a series of strategies that will help them to learn about and enjoy the network while preventing risks and detecting possible problems. At this point, it is necessary to earn their trust day by day, and get involved in their online environment:
- Active strategies: You must be aware of their day-to-day life on the internet, learn about the apps they like and their online contacts and friends. All that should take place in an environment of total trust, where the minor feels free to tell you about any problem. In addition, it is also recommended to share online activities together so that you accompany them and spend quality time on the Internet together, and guide them to enhance their social skills and critical thinking.
- Restrictive strategies: Children must also understand the rules and limits imposed. For this, the rules must be coherent, consistent, and agreed on. For example, it must be established how long and in what places they can use the internet. Also, regarding the pages and apps of common use, configure the privacy options on social networks together.
- Family agreements for the proper use of devices: Through these defined agreements, the rules for using the internet as a family can be clearly established. These may include social networks, video consoles, tablets, mobiles, or devices shared between relatives.
Beware of connected toys:
Connected toys can bring additional advantages, but also some dangers, such as the use that the toy makes of the information collected, the risk that it is not safe enough and an outsider manages to connect and interact with the child or that they misuse any recording without permission. The risks are many, so it is necessary to take into account the following advice:
- Evaluate the recommended age for the toy and, if you buy it, accompany the minor during the game to show them how to play responsibly and safely, and how they can ask for help. Also, teach them not to say or do anything in front of the toy that they do not want a stranger to hear or see.
- Read the technical description to find out what its features are, security measures, availability of updates, and if it has any type of parental control. It is also recommended that you completely disconnect the toy when it is not in use.
- If the toy connects to another device, set it up securely and improve the security of the WiFi connection to block access to other people.
If your kid plays games on the internet, teach them not to open or click on the links sent by any unknown person. Better to check their identity on Nuwber. Often, strangers pose as fellow gamers to gain kids’ trust and scam them later.
Use parental control tools:
There are many programs and devices with parental control features. These tools give parents the ability to limit device usage and control what it's doing to provide kids with a safe way to enjoy technology. Among the functionalities offered by these tools, the following stand out:
- Control the time of use of the device.
- Content filtering and application blocking.
- Activity tracking.
- Geolocation.
- Alerts and notifications.
How to adapt to each age?
Depending on each age, it is necessary to take some measures aimed at learning to use the Internet safely and creating an environment of trust:
- 0 to 2 years: Avoid or limit contact with screens, be it computers or television.
- 3 to 5 years: Establish rules from the beginning and limit access to short periods. Carefully select the content your child consumes. Accompany them during the activity with explanations appropriate to their understanding. Set parental controls on the devices you use.
- 6 to 9 years: Limit connection times. Teach them to identify positive and quality content for their age. Track or monitor their activity and their contacts. Show them how to search for information, and that not everything is true on the internet.
- 10 to 13 years: Adapt connection times to their age and maturity. You should supervise the contents, contacts, and activity on social networks.
- 14+ years: Adapt the usage agreement and connection times to their needs and maturity. Guide them towards positive content for their education and entertainment. Encourage them to talk to you openly about their daily activity on the internet. Foster their critical thinking and maintain a climate of communication and trust.
Do you still have a problem with the internet?
If the minor is in trouble because of something that has happened on the internet, the first step is to stay calm and focus on finding solutions. Do not be afraid to ask for help, there are various establishments prepared to help with these problems:
- The educational center can advise on the management of the problem, mediate between the parties, or even intervene directly. In addition, they can also offer psychological and educational help if necessary.
- The health center can treat the negative effects of an online problem, either physically or psychologically.
- Social networks and other platforms on the internet can manage our requests to remove content and block users. In their "security centers," they offer information about it.
- The police forces can advise on the problem and process the complaint since they usually have units specializing in computer crimes.




Comments